In recent years, solar energy has become increasingly popular as a clean and sustainable power source. With technological advancements, several types of solar panels are available on the market.
However, choosing the right type of solar panel for your company’s needs can be daunting. To help you make an informed decision, we will explore the different types of solar panel and their efficiency, their advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for various use cases.
Understanding Solar Panels

Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, also known as photovoltaic or PV panels. They are composed of individual solar cells made from silicon, boron, and phosphorus layers.
When sunlight strikes the panel’s surface, it creates an electric field that generates a directional current, which is then harnessed as usable power.
1. How Solar Panels Work
The process by which solar panels convert sunlight into electricity is known as the photovoltaic effect. Each solar panel consists of multiple solar cells, usually 60, 72, or 90 cells.
These cells are made from silicon layers, with a boron layer providing a positive charge and a phosphorus layer providing a negative charge. Electrons are knocked loose when photons from the sun’s rays hit the silicon layers, creating an electric current.
2. The Importance Of Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency refers to the amount of sunlight that can be converted into electricity. The higher the efficiency, the more electricity is generated from the same amount of sunlight.
Improvements in photovoltaic technology have led to higher efficiency rates, with current solar panels ranging from 15% to 22% efficiency. High-efficiency panels can even reach nearly 23%.
3. Factors Affecting Solar Panel Efficiency
The efficiency of a solar panel is influenced by two main factors: photovoltaic (PV) cell efficiency and total panel efficiency. The cell design, silicon type, and layout and configuration of the cells determine PV cell efficiency.
Total panel efficiency takes into account the maximum power rating under standard test conditions divided by the total area of the panels.
Types Of Solar Panels
Several types of solar panels are available on the market, each with unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Take a look at the four different types of solar panels: monocrystalline, polycrystalline, PERC, and thin-film panels.
1. Monocrystalline Solar Panels
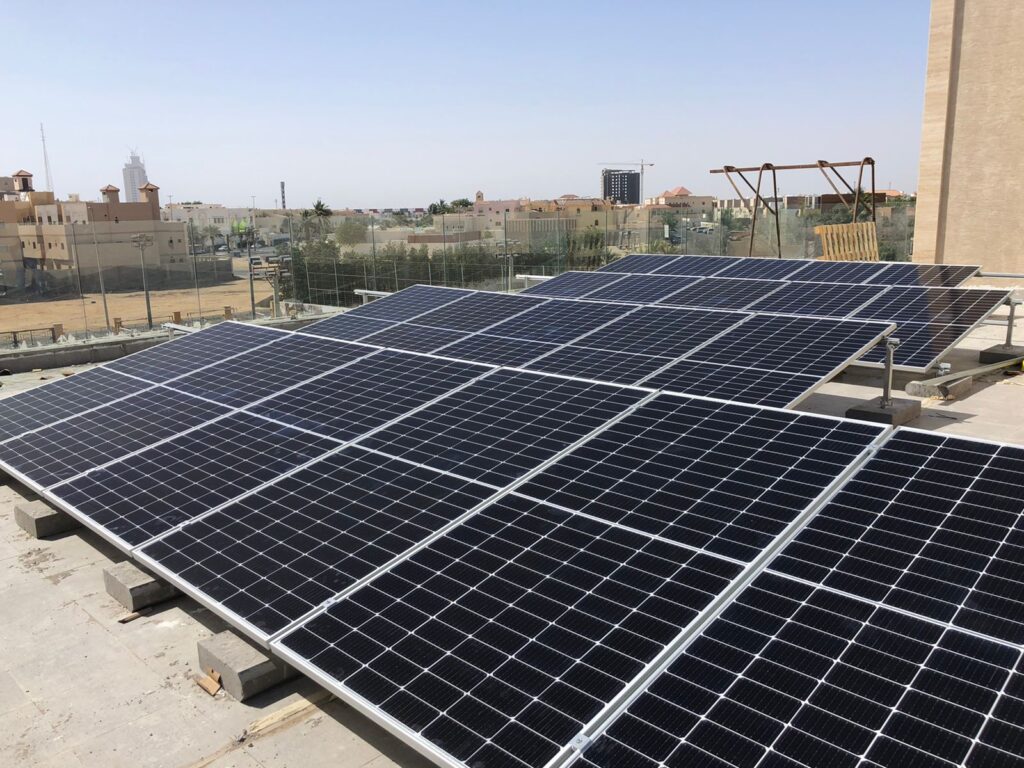

Monocrystalline solar panels, also known as single-crystal panels, are made from a single pure silicon crystal cut into several wafers.
These panels are easily identifiable by their dark black color. Monocrystalline panels are known for their high space efficiency and long lifespan. They have the highest efficiency among all types of solar panels, typically ranging from 15% to 22%.
However, the production process for monocrystalline panels results in a significant amount of silicon wastage, leading to higher production costs. This makes monocrystalline panels more expensive compared to other types.
2. Polycrystalline Solar Panels
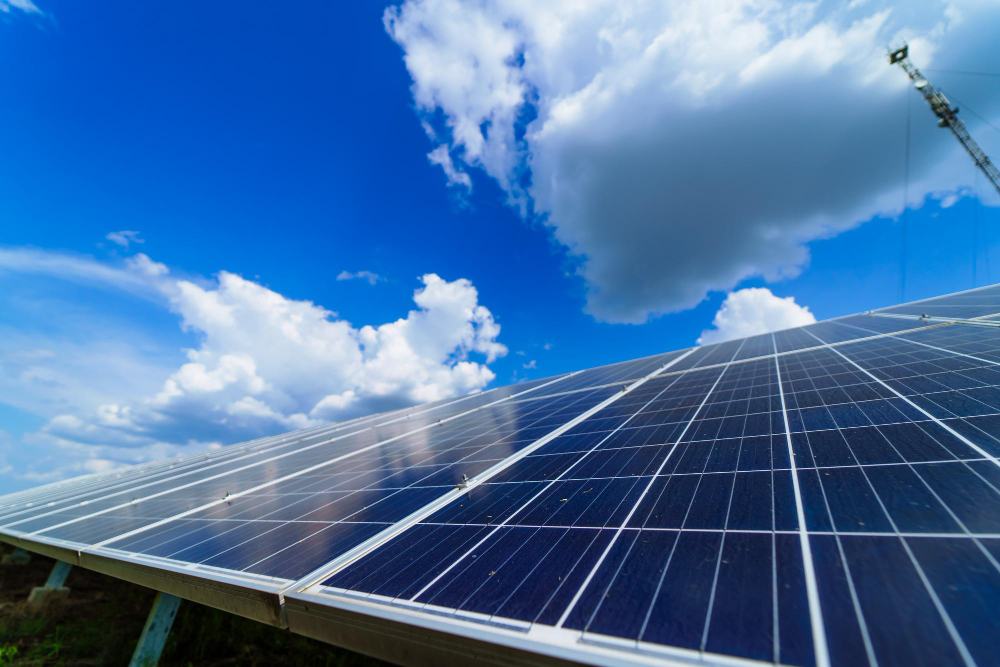

Polycrystalline solar panels are made from multiple silicon crystals instead of a single crystal. The silicon fragments are melted and poured into a square mold, giving polycrystalline cells their characteristic square shape.
These panels are more affordable than monocrystalline panels due to the reduced wastage of silicon during production. However, the lower silicon purity and construction of polycrystalline panels result in lower energy conversion efficiency of 15-17% compared to monocrystalline panels.
They also have lower heat tolerance, making them less efficient in high-temperature environments.
3. PERC Solar Panels
Passivated Emitter Rear Cell (PERC) solar panels are an advanced type of solar panel incorporating a rear passivation layer. This layer reduces electron recombination, leading to improved efficiency.
PERC panels typically have higher energy conversion rates than traditional monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels. The enhanced efficiency of PERC panels comes at a slightly higher cost than standard monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels.
However, the increased efficiency can result in higher overall energy production, making them a popular choice for commercial and industrial applications.
4. Thin-Film Solar Panels

Thin-film solar panels are made by depositing fragile layers of semiconductor material onto a substrate, such as glass or plastic. This production method allows for flexibility and versatility in the shape and size of the panels.
Thin-film panels are lightweight and can be used in unconventional applications, such as curved surfaces or portable solar devices. However, thin-film panels have lower energy conversion efficiency compared to crystalline panels, typically ranging from 10% to 12%.
Besides, they also require a larger surface area to generate the same amount of electricity as crystalline panels. Thin-film panels, such as large-scale solar farms, are often used in projects where space is not a constraint.
Choosing The Right Solar Panel For Your Company

Several factors must be considered when selecting the right solar panel for your company. Take a look at some key considerations:
1. Efficiency
If maximizing energy production is a priority, then high-efficiency panels like monocrystalline or PERC panels may be the best choice.
These panels have the highest energy conversion rates and can generate more electricity in limited space.
2. Cost
Cost is often a significant factor for businesses considering solar panel installations. Polycrystalline panels are generally more affordable compared to monocrystalline and PERC panels.
However, it’s essential to consider the long-term benefits and potential energy savings when evaluating the overall cost-effectiveness of different panel types.
3. Available Space
The amount of available space for solar panel installation is an important consideration. If space is limited, high-efficiency panels like monocrystalline or PERC panels can generate more electricity per square meter.
On the other hand, if space is not a constraint, thin-film panels may be a suitable option due to their flexibility and more extensive surface area requirements.
4. Specific Use Case Requirements
Different industries and applications have varying requirements for solar panel installations. For example, if your company operates in a high-temperature environment, panels with higher heat tolerance, such as monocrystalline or PERC panels, may be more suitable.
If your company requires portable solar solutions, thin-film panels offer flexibility and lightweight options.
Conclusion
Choosing the best type of solar panel for your company is crucial to maximizing energy production, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for specific use cases. Understanding the different types of solar panels, their advantages, disadvantages, and key considerations will help you make an informed decision.
Whether you opt for high-efficiency monocrystalline panels, cost-effective polycrystalline panels, advanced PERC panels, or versatile thin-film panels, transitioning to solar energy can benefit your company and contribute to a greener future.





